Understanding RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) doesn’t have to be technical or intimidating. Even the most complex RAID levels can be easily grasped with the right analogies and everyday examples. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, IT professional, or just curious about how data protection and speed enhancements work in storage systems, this guide breaks it down clearly and practically.
What Is RAID and Why Does It Matter?
RAID combines multiple physical hard drives into one logical unit for redundancy, performance, or both. Depending on the RAID level, you can improve data access speed, protect against disk failure, or strike a balance between the two.
Different RAID levels use various strategies for organizing and protecting data. Let’s explore the most commonly used RAID configurations, enriched with relatable analogies and real-world examples.
RAID 0 – Striping for Speed
Analogy
Imagine you’re writing an extended essay and you divide every other sentence between two friends to type. They both work simultaneously, finishing the essay twice as fast.
Real-World Example
You split the chapters of a book between two people. One handles odd-numbered chapters, the other even-numbered. The book gets typed up in record time.
Key Point
RAID 0 prioritizes speed. Data is divided (striped) evenly across two or more disks. This setup offers faster read/write performance and is ideal for gaming, video editing, and large file handling.
However, there’s no data redundancy. If even one drive fails, all data is lost.
RAID 1 – Mirroring for Safety
Analogy
You create two identical copies of your family photo album and give one to each of your two best friends. If one loses it, the other still has an exact duplicate.
Real-World Example
Photocopy your passport and keep one copy at home while traveling with the other. If one is lost, you still have a fallback.
Key Point
RAID 1 focuses on redundancy. All data is copied (mirrored) from one drive to another. If one disk fails, the system continues to operate using the mirror.
You get high data safety, but storage capacity is halved—you only get the capacity of one disk, as everything is duplicated.
RAID 5 – Speed with Single Parity Protection
Analogy
You distribute different parts of a document to three friends and include a “cheat code” that lets any two reconstruct the third friend’s missing portion.
Real-World Example
Three students take notes in class, with each writing on different topics. One also writes a summary formula. If one is absent, the others use the summary to recreate what’s missing.
Key Point
RAID 5 strikes a balance between speed and safety. It uses block-level striping and distributes parity data across all drives.
If one drive fails, the system can rebuild the lost data using parity. However, if two drives fail, data loss is irreversible. Ideal for general-purpose servers and network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
RAID 6 – Extra Parity for Extra Protection
Analogy
You repeat RAID 5’s system, but now with two cheat codes. The notes can still be rebuilt even if two friends lose their data.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re planning a trip and make three copies of your packing list: two backups in different bags. Even if you lose two, the remaining one ensures you’re still covered.
Key Point
RAID 6 builds on RAID 5 by adding double parity, allowing the array to survive the failure of any two drives.
It offers better fault tolerance than RAID 5 but requires more storage for parity and performs slightly slower due to the additional calculations.
RAID 10 (1+0) – Mirrored Striping for Speed and Redundancy
Analogy
You divide a project among two teams (striping) and then make each team duplicate their part (mirroring). You now have both speed and protection.
Real-World Example
Think of two pairs of friends. Each pair has half the book, but both members have identical copies. Work gets done quickly, and you still have backups.
Key Point
RAID 10 is a hybrid RAID combining the best of both RAID 0 and 1. It stripes data across multiple mirrored pairs. You get fast performance and strong redundancy.
This configuration requires a minimum of four drives, but it’s one of the best options for mission-critical systems where performance and data integrity are equally vital.
Performance vs Redundancy: How to Choose the Right RAID
Choosing the right RAID level depends on your use case, budget, and risk tolerance. Here’s a quick guide:
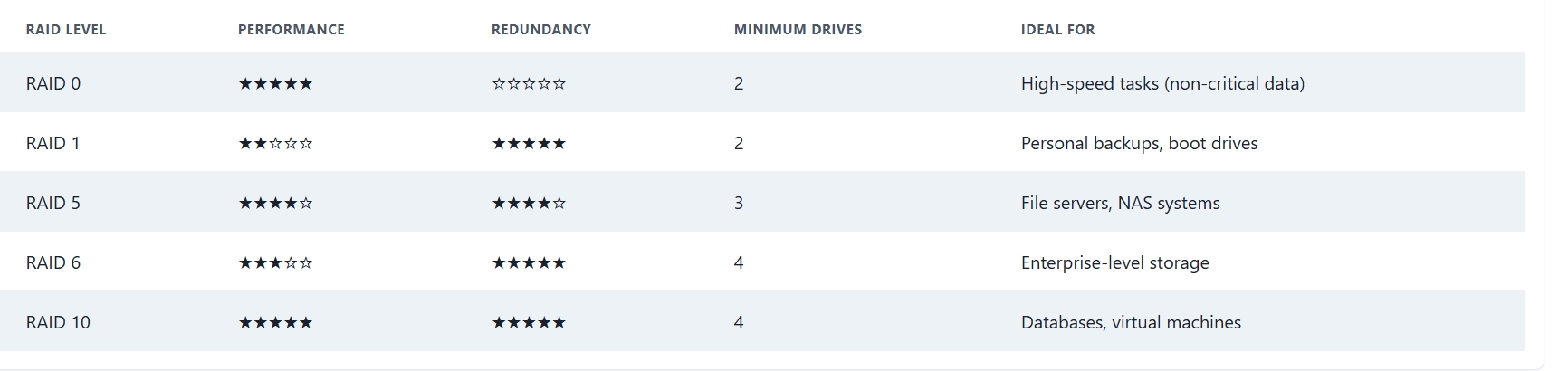
Important Notes About RAID
- RAID is not a backup: It protects against hardware failure, not accidental deletions or malware. Always maintain external backups.
- Use enterprise-grade disks: RAID setups work best with disks designed for continuous operation and RAID environments.
- RAID controllers matter: A reliable hardware RAID controller can dramatically improve performance and reliability.
RAID in the Real World: Where You See It
- Data Centers: RAID 10 and RAID 6 ensure uptime and prevent data loss.
- Media Production: RAID 0 for fast read/write editing of 4K or 8K video files.
- Corporate Servers: RAID 5 and 6 for a performance and fault tolerance balance.
- Personal NAS Devices: RAID 1 or 5 setups used by content creators and small business owners.
Wrap Up: RAID as a Strategic Data Tool
Think of RAID as a team strategy for managing your data. You can split the workload for faster results, duplicate everything for safety, or find the perfect middle ground that offers both.
Like choosing how many friends to involve and how to split a task among them, selecting a RAID level optimizes speed, safety, and efficiency. Once you understand these core ideas, RAID becomes not just a tech term, but a smart strategy in managing digital information.

Selva Ganesh is a Computer Science Engineer, Android Developer, and Tech Enthusiast. As the Chief Editor of this blog, he brings over 10 years of experience in Android development and professional blogging. He has completed multiple courses under the Google News Initiative, enhancing his expertise in digital journalism and content accuracy. Selva also manages Android Infotech, a globally recognized platform known for its practical, solution-focused articles that help users resolve Android-related issues.





I’m a student and this is a perfect summary for my IT class.
The examples were a great touch. Very practical and easy to grasp.
I now understand the difference between hardware and software RAID. Big help!
This is a great starting point for anyone considering a RAID setup.
The explanation of how data is distributed across disks is fascinating.
Thank you for breaking down such a complex topic so simply.
This article made me feel more confident about setting up my own home server.
The section on RAID 1+0 (or RAID 10) was particularly helpful for my needs.
Is there a performance hit with using RAID for data redundancy?
I’m glad I read this before I bought my drives. I was about to make a huge mistake.
This is a much better explanation than what I found on Wikipedia.
The part about rebuilding a failed drive was very detailed and useful.
What is the biggest mistake people make when setting up a RAID system?
Excellent article. The analogy of the RAID 5 as a checkerboard is very clever.
I’m a photographer and this helped me understand how to protect my photo library.
This guide is fantastic for anyone new to server administration.
The diagrams and visuals would be a great addition to this already excellent article.
I appreciate the focus on both data protection and performance. A balanced view.
This article helped me decide on a RAID 10 setup for my small business. Thank you for the insights!
Is it possible to mix different sized drives in a RAID array?
I’ve been looking for an article like this for ages. Perfect!
Very informative! The explanation of data stripping was very easy to follow.
Could you write a similar guide about NAS (Network Attached Storage)?
I’m an IT student, and this is a great resource for my class. Thank you!
The simplicity of this guide is what makes it so good. No technical jargon.
I wish I had read this before buying my external hard drives. I could have set up a better system.
The article is very well-structured. It flows logically from one topic to the next.
The analogy of RAID 1 as a mirror is perfect. So easy to remember now.
I’ve bookmarked this for future reference. Great job!
Very clear and concise. This is the best RAID explanation I’ve found online.
Could you explain how to set up RAID on different operating systems?
The real-world examples were my favorite part. Makes it easy to relate to.
Is RAID still relevant with SSDs? This article mostly talks about HDDs.
A must-read for anyone building a new computer or server.
The part about read/write speeds was particularly insightful.
What about nested RAID levels like RAID 10? Could you cover that in another article?
This article convinced me to finally set up a RAID 1 array for my home server. Thank you!
I’ve been working with servers for years and still learned something new from this. Well written.
The chart comparing the different RAID levels is a fantastic summary. Very helpful.
The explanation of parity was a lifesaver. This will help a lot with my next project.
I never knew RAID 0 was so risky. Good to know the trade-offs now.
Great guide for beginners. The real-world examples are spot on.
I’ve always been confused about RAID 5 vs RAID 6, but this article makes it so much clearer. Thanks!
This is an excellent breakdown of RAID! The analogies really help clarify the different levels.